In this article
- The Relentless Growth of Phishing Attacks
- 17 Easy Hacks to Prevent a Phishing Attack
Blog Articles
Article at a glance
Phishing attacks are increasingly sophisticated and can lead to severe data breaches if not handled properly:
- Common phishing tactics include deceptive emails, malicious links, and fake websites designed to steal sensitive information.
Protect yourself by scrutinizing email sources, avoiding clicking on suspicious links, and educating your team on recognizing phishing attempts. What is the solution?
Read more
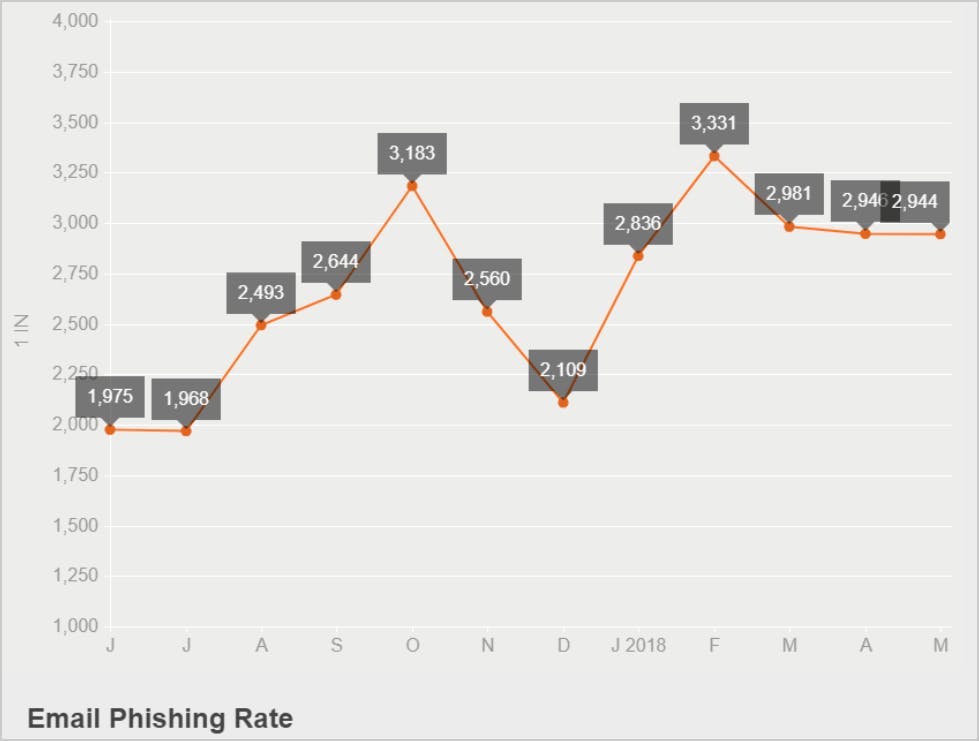
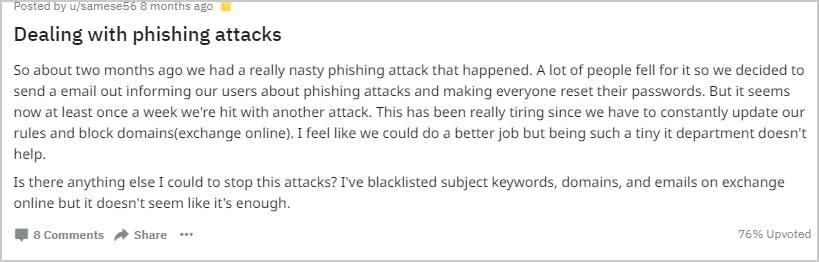
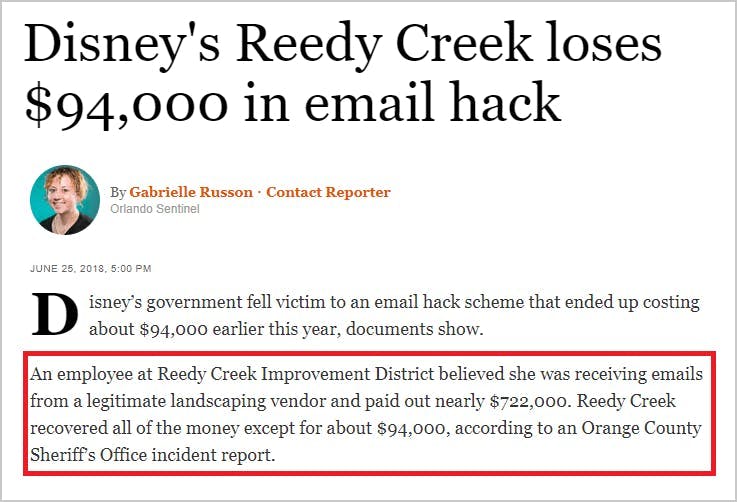
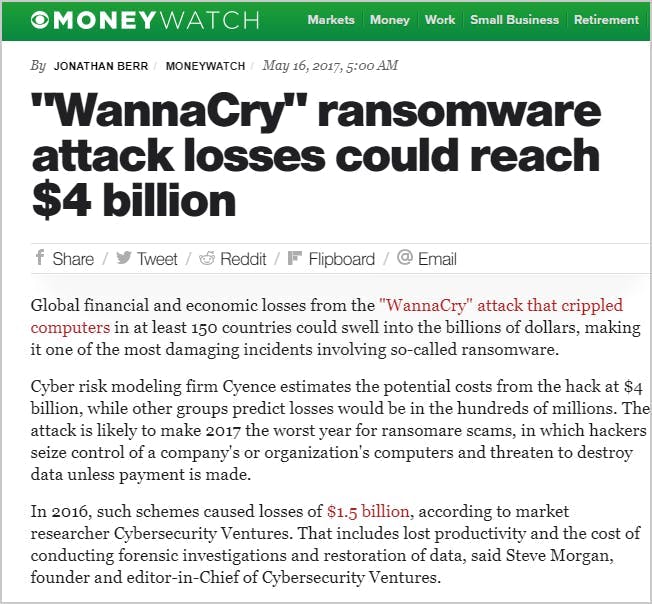
The relentless growth of phishing attacks
What are the different types of phishing attacks?
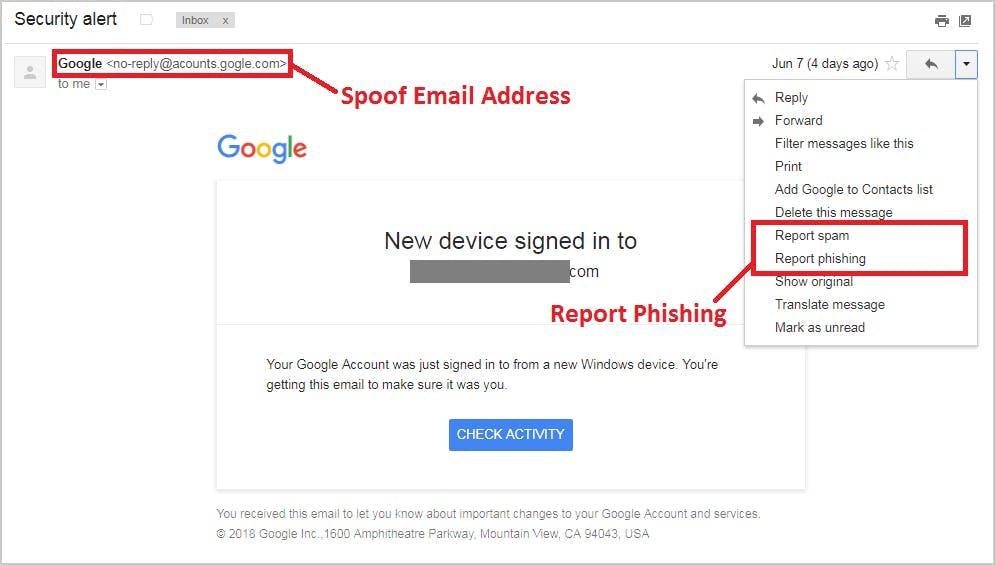
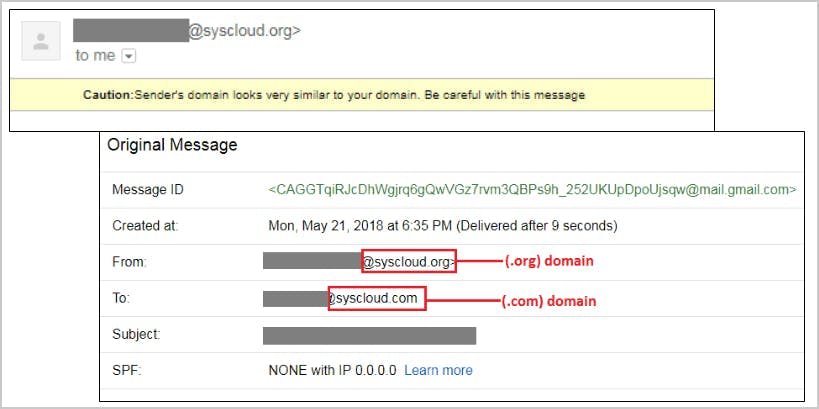
1. Business domain impersonation
2. Brand impersonation
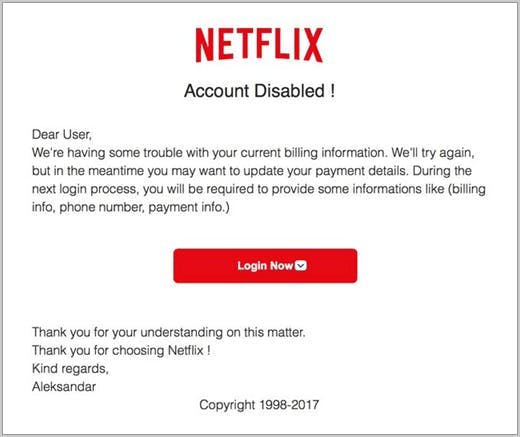
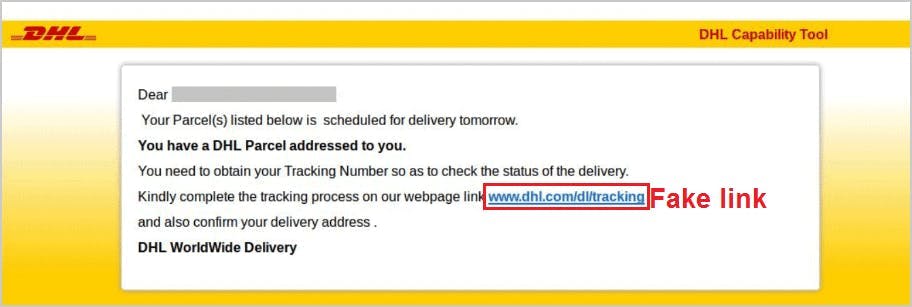
3. Suspicious link
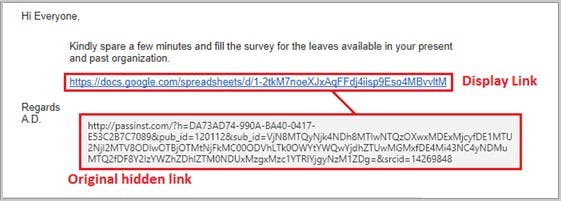
4. Name impersonation
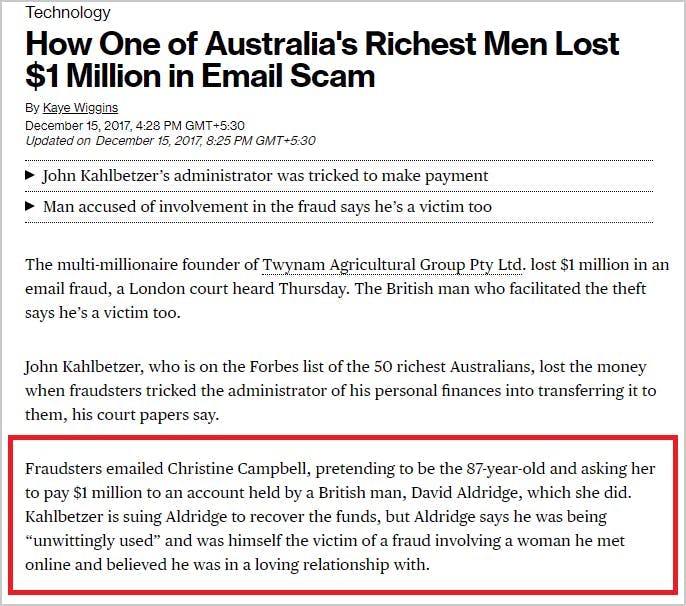
5. Content injection

6. Man-in-the-middle attack
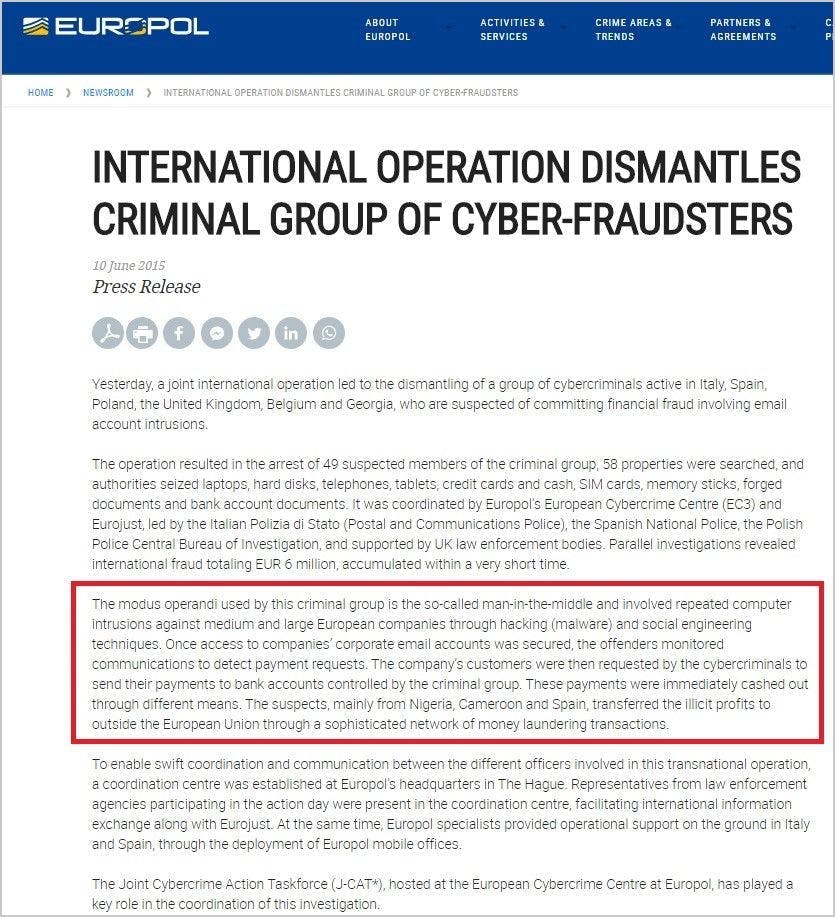
7. Search engine attack
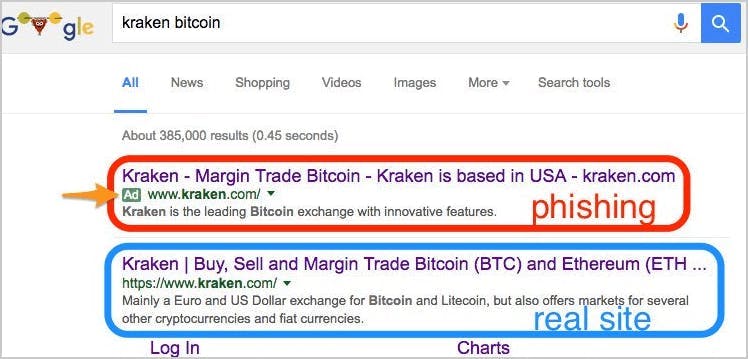
17 easy hacks to prevent a phishing attack
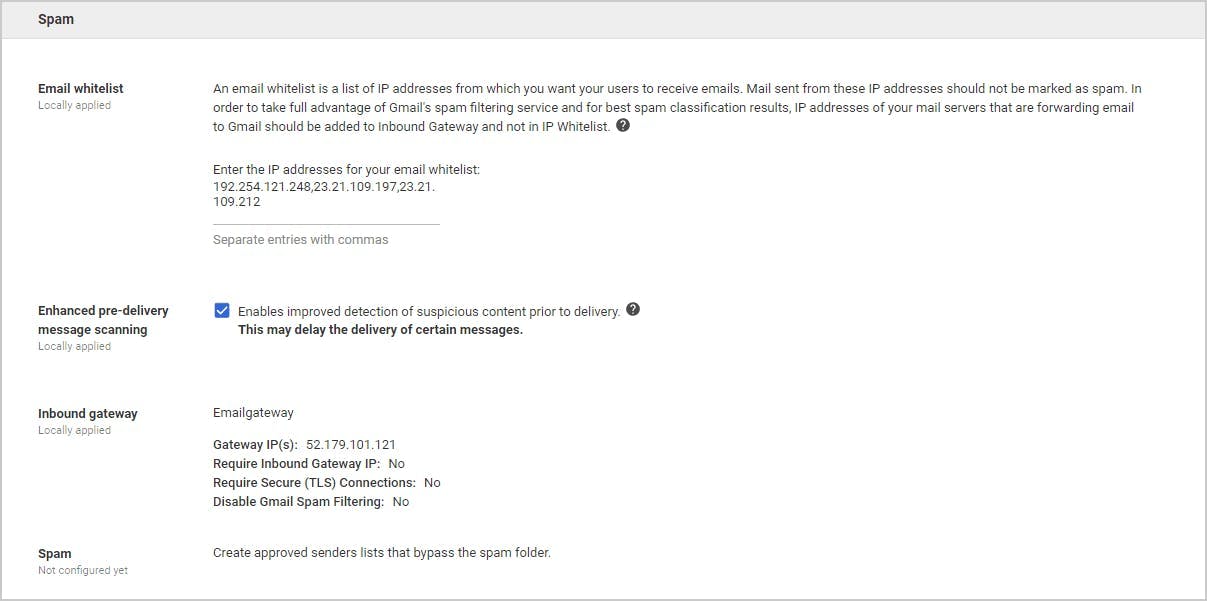
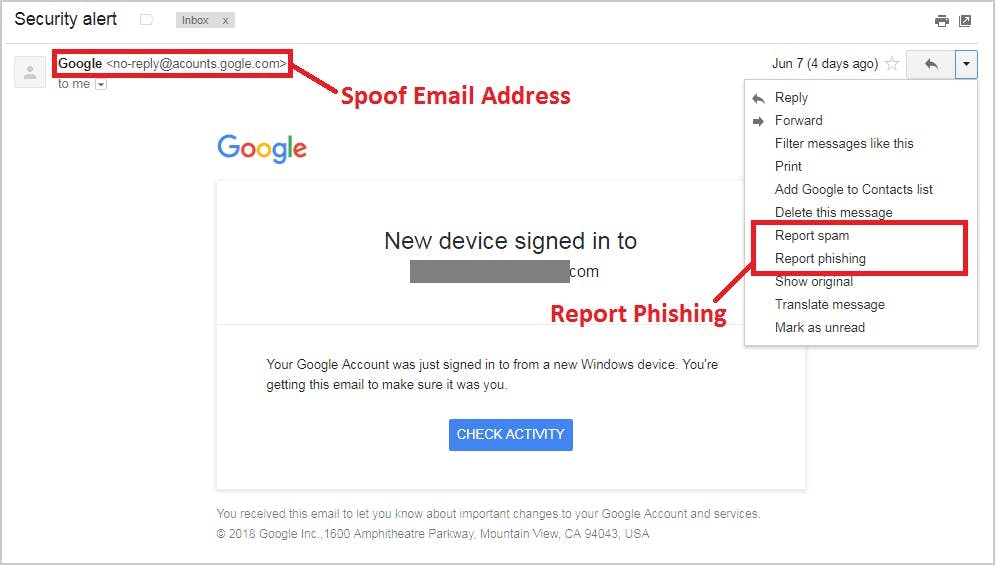
1. Use spam filter for Gmail and Microsoft 365/Outlook
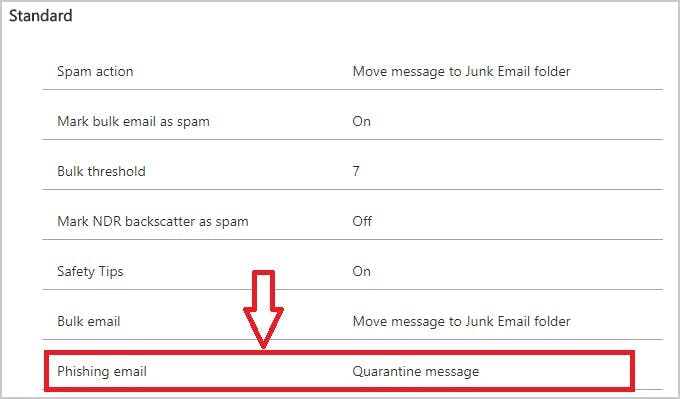
2. Use multi-factor authentication
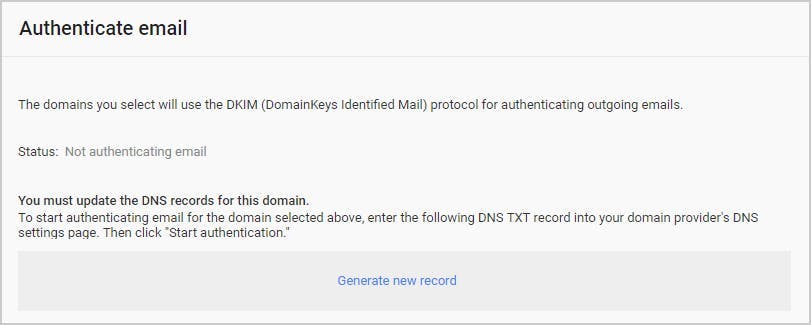
3. Configure email for secure data flow
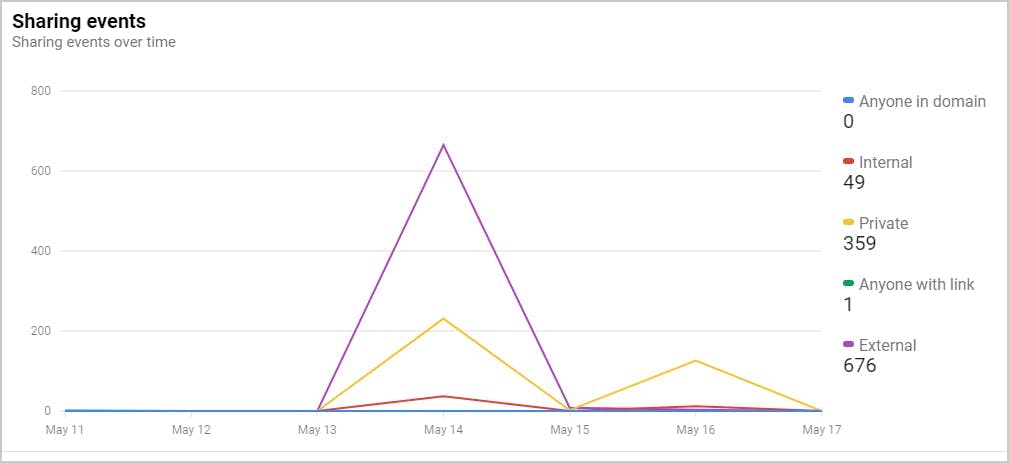
4. Monitor suspicious external sites
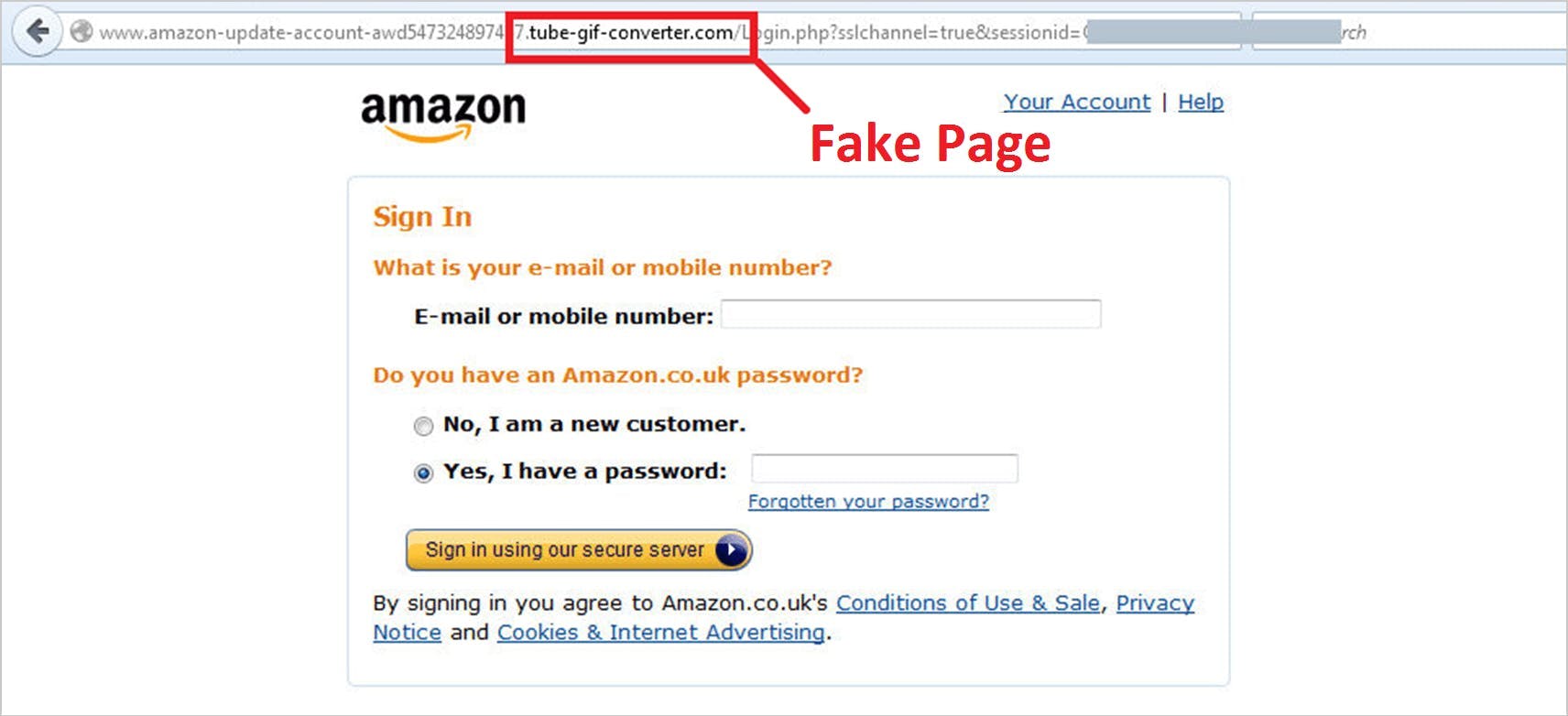
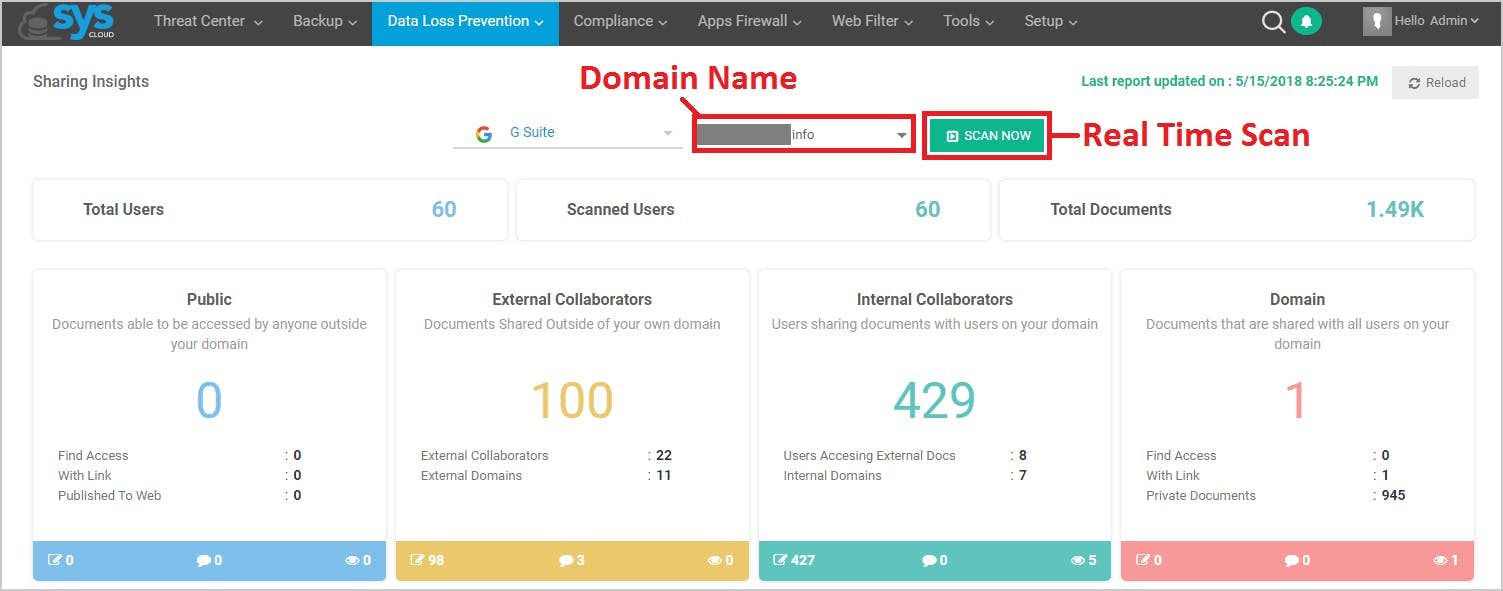
5. Perform real-time scan
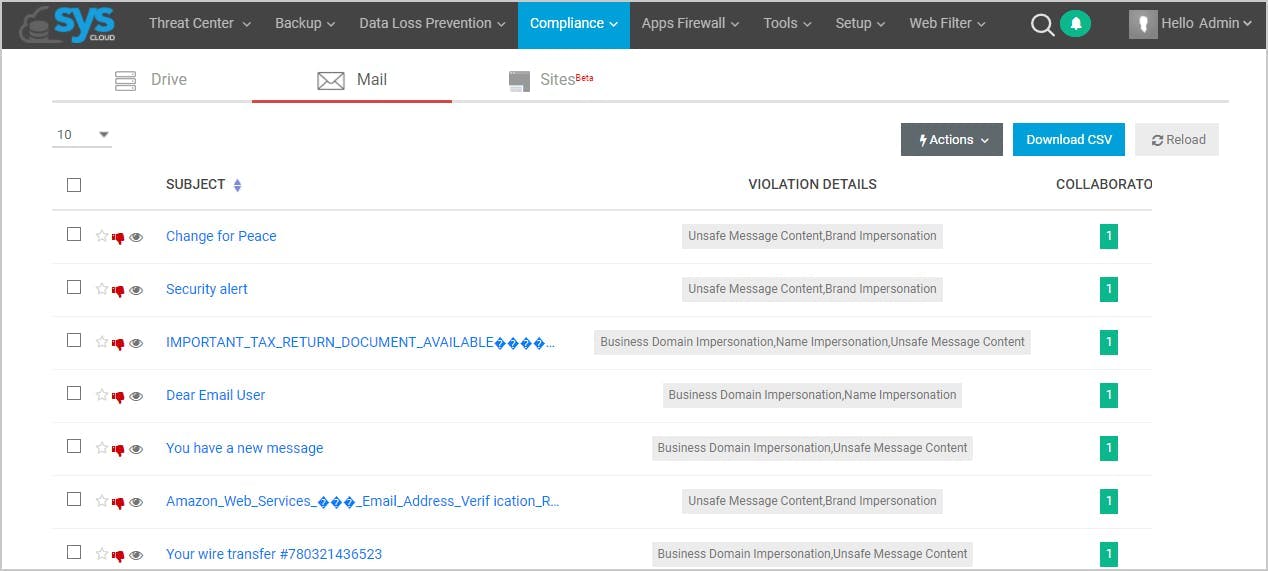
6. User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA)
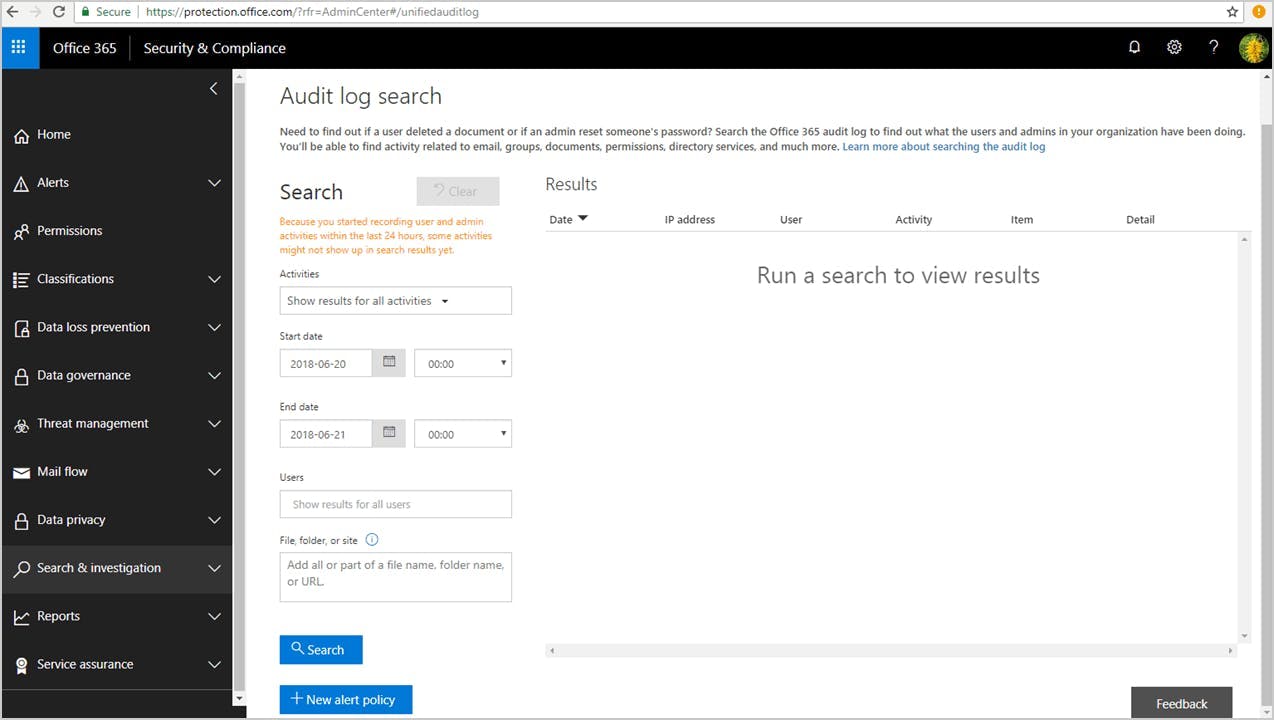
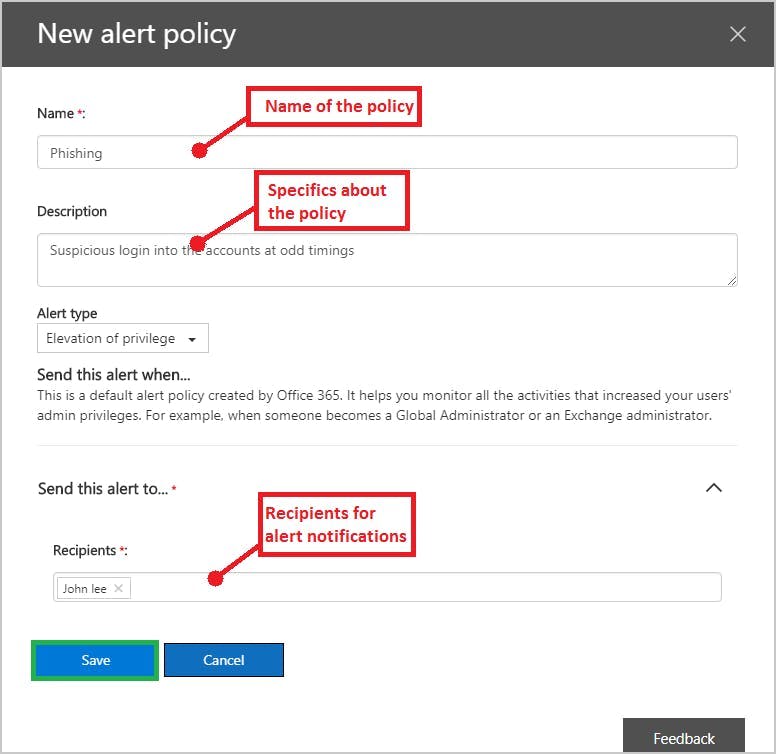
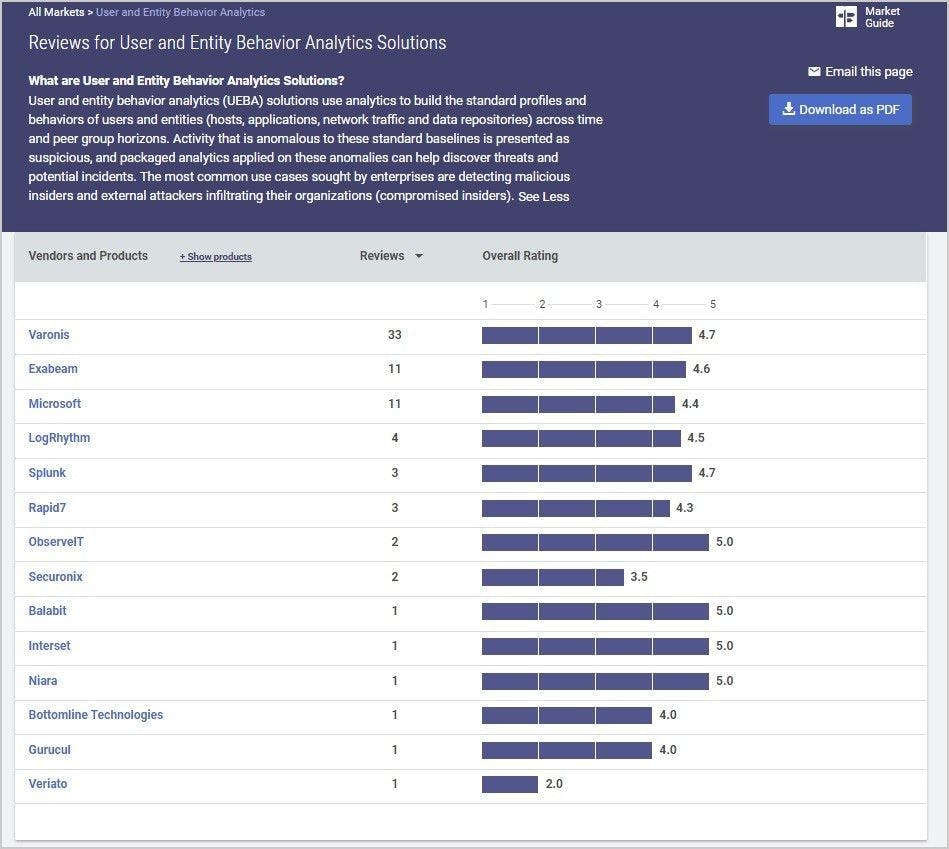
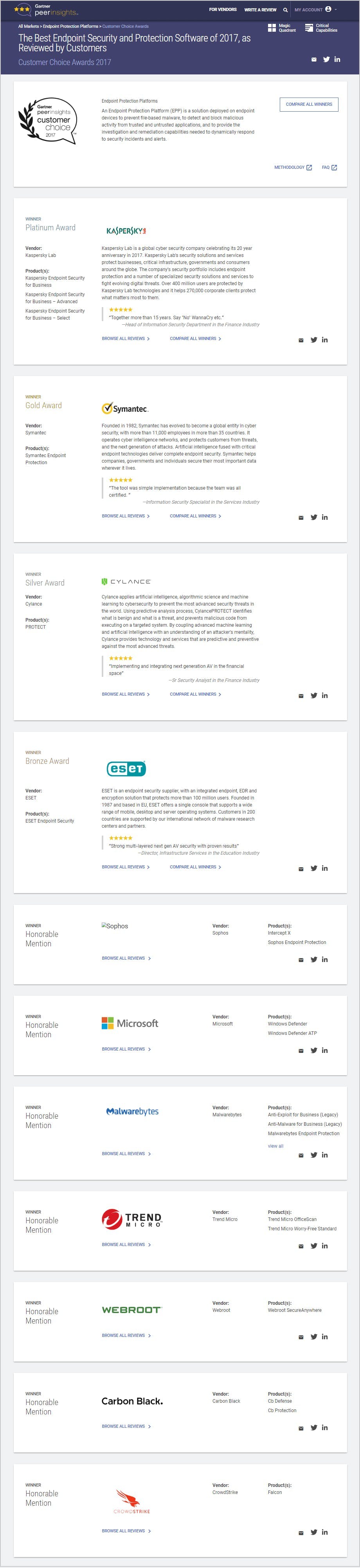
7. Implement solutions for malware and spyware
8. Implement secure document sharing
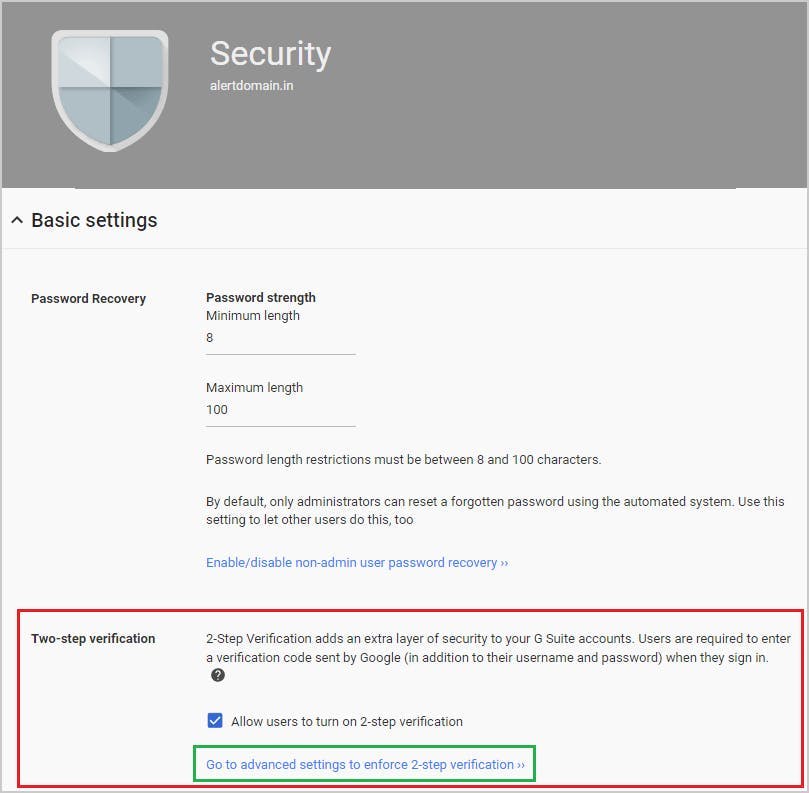
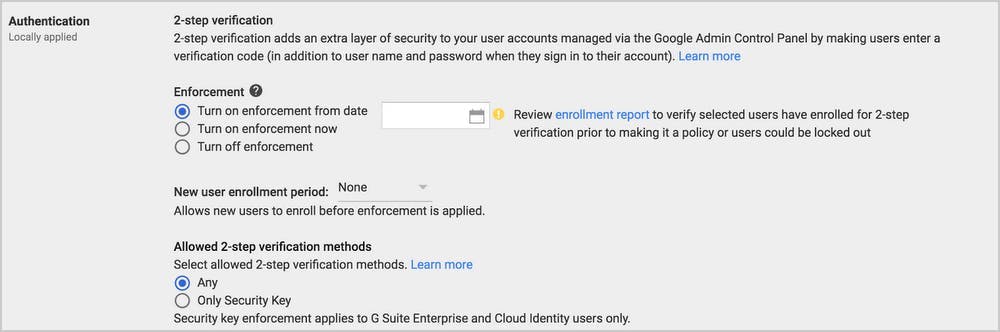
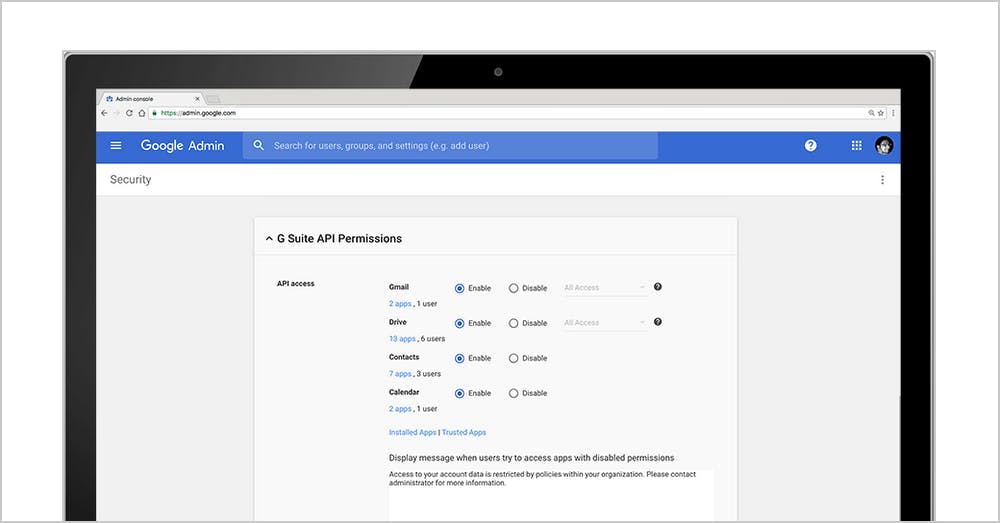
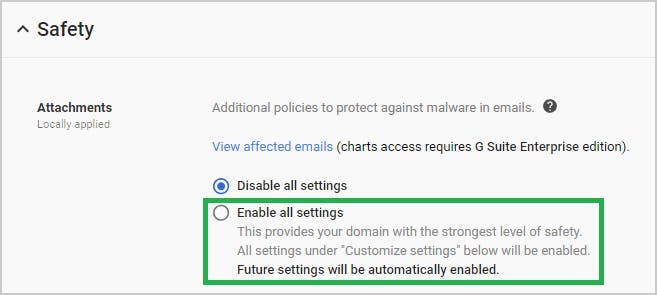
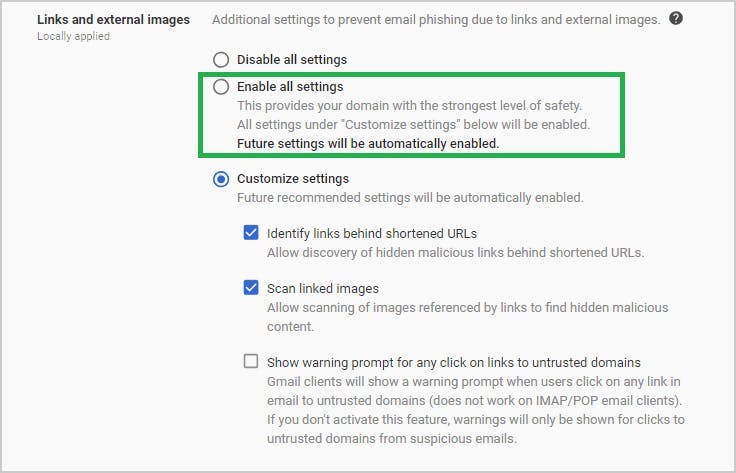
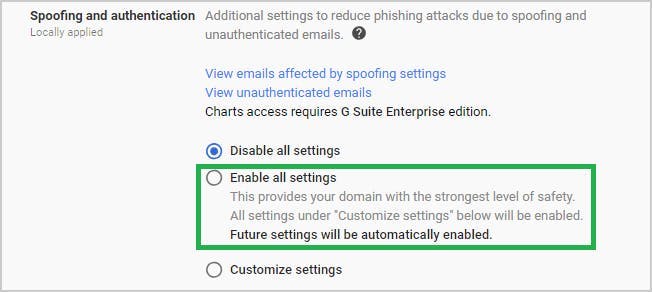
9. Prevent phishing on your G-Suite domain
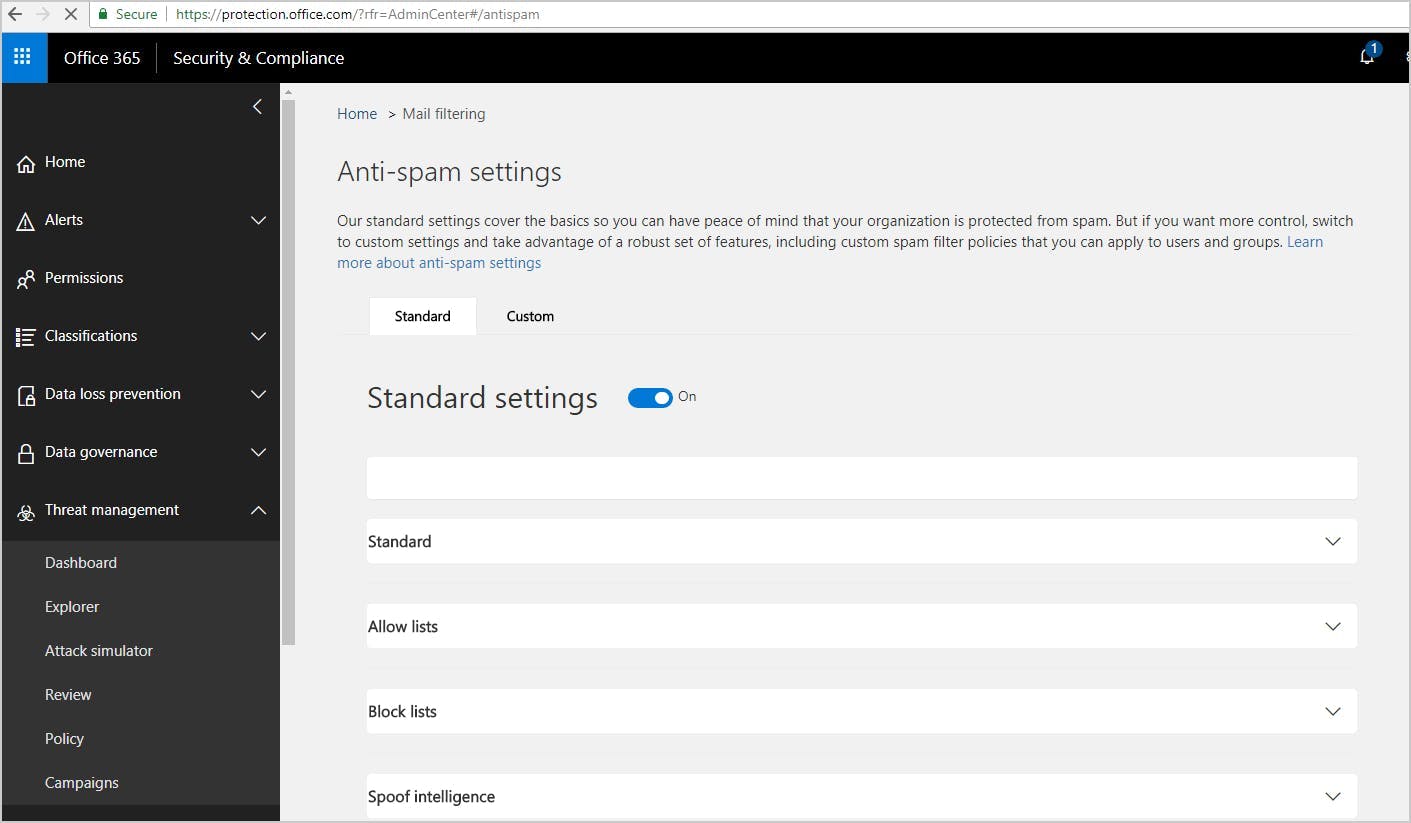
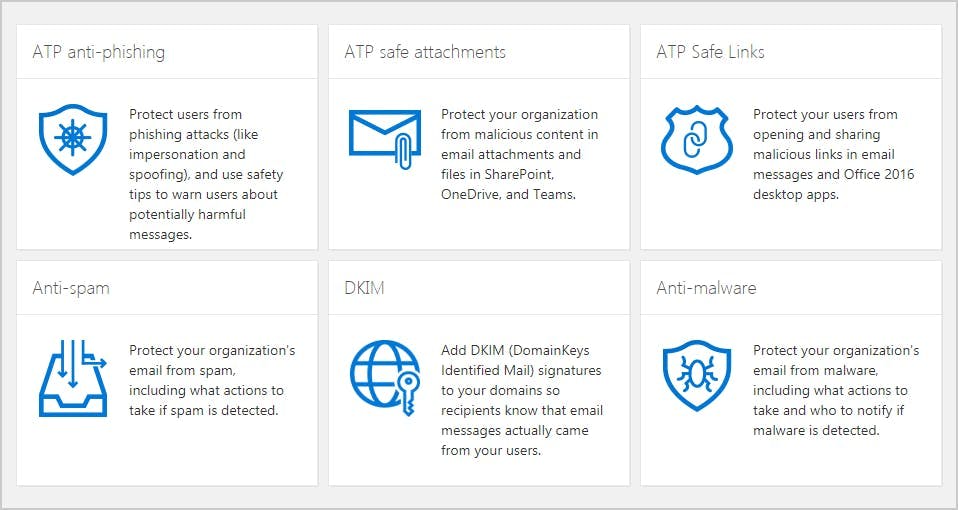
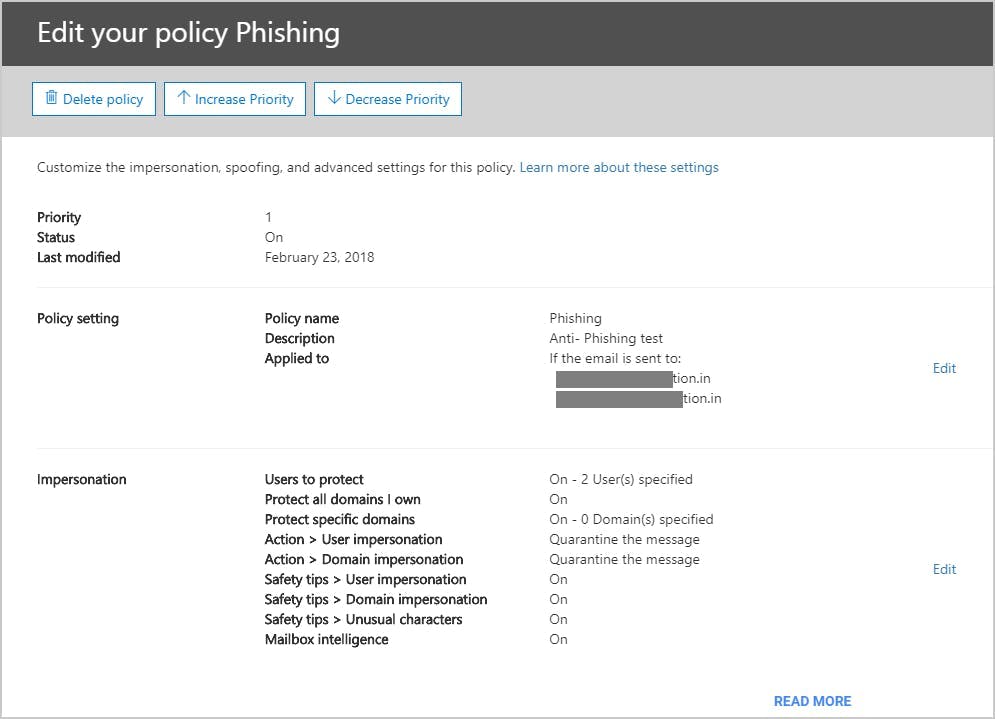
10. Enable Office 365 phishing protection
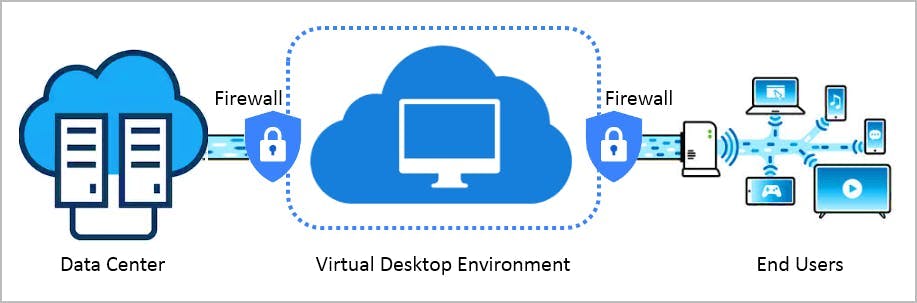
11. Enable secure browsing with virtual desktop infrastructure
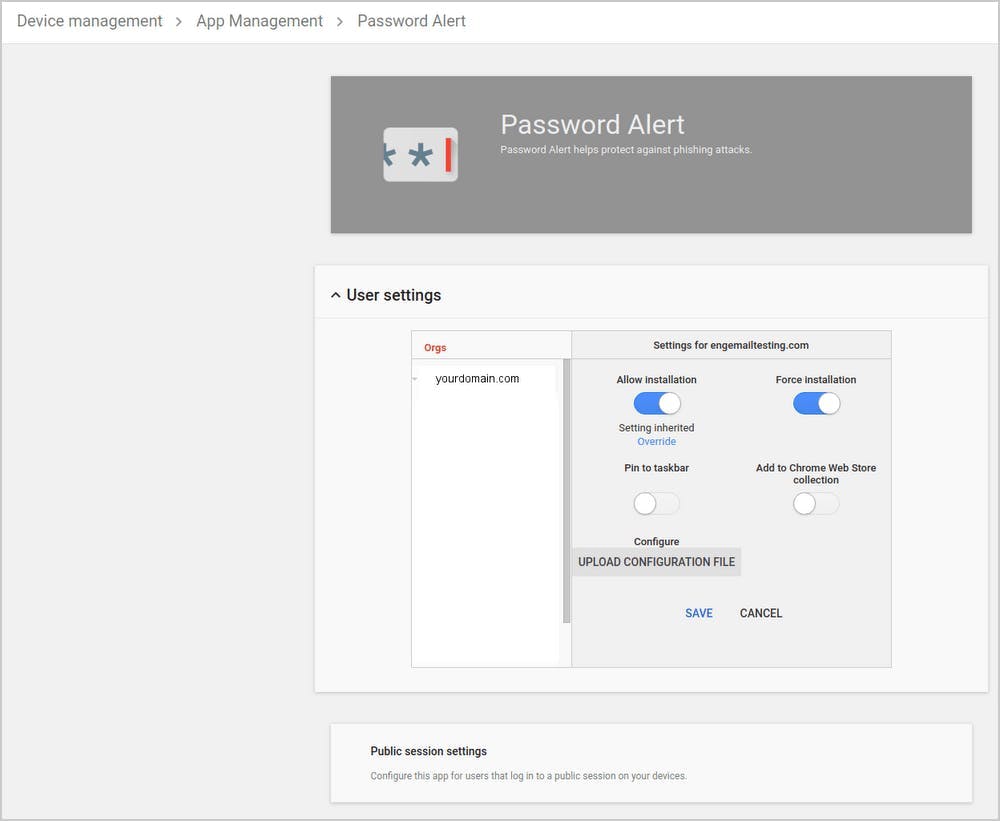
12. Deploy password alert extension for G Suite
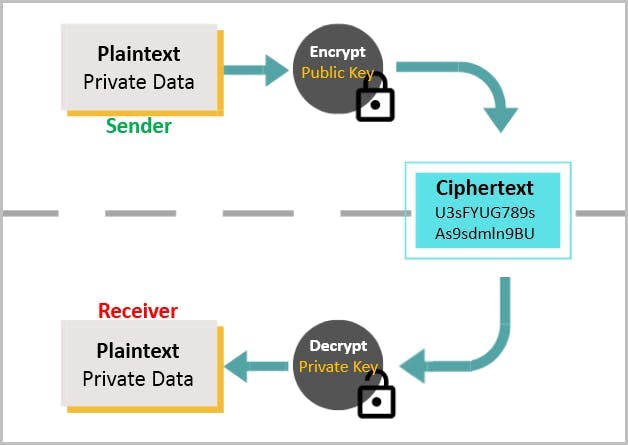
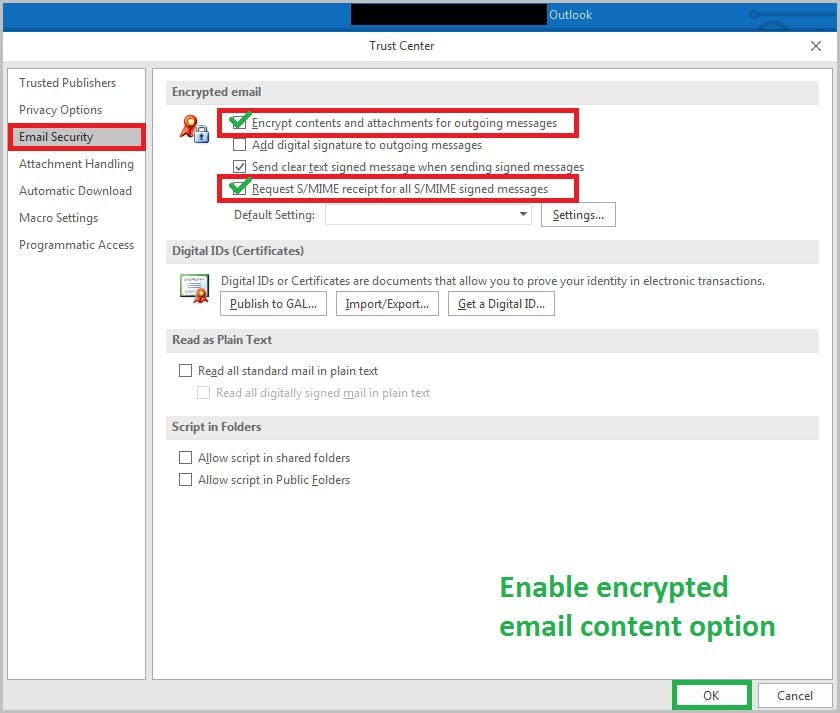
13. Use encryption for data transmission
14. Enable OAuth
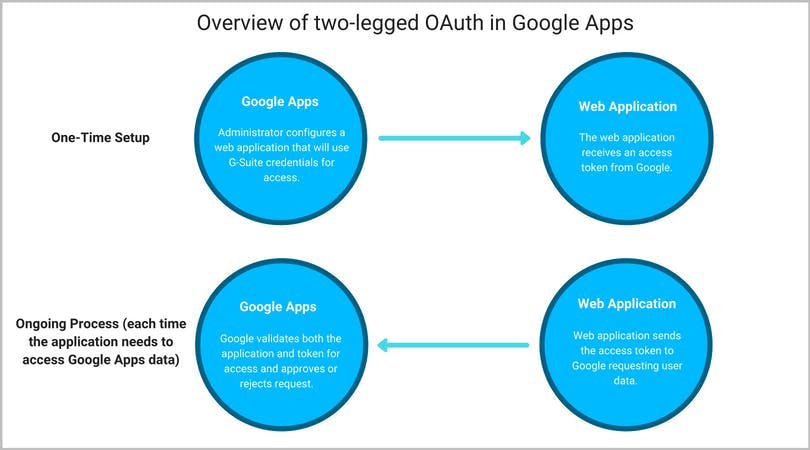
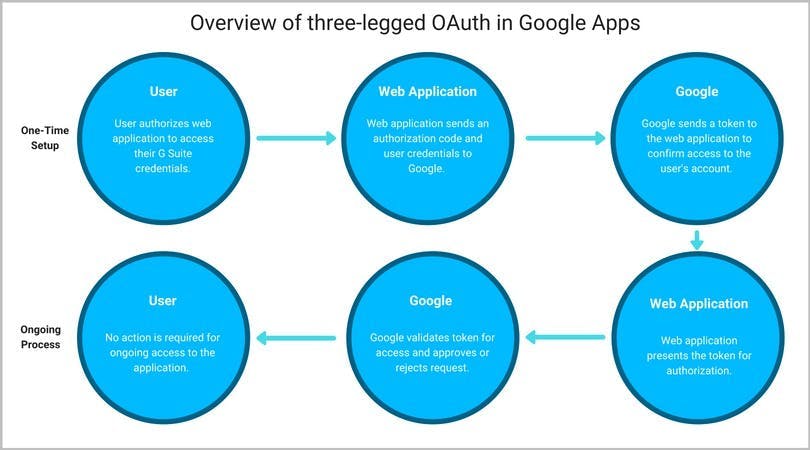
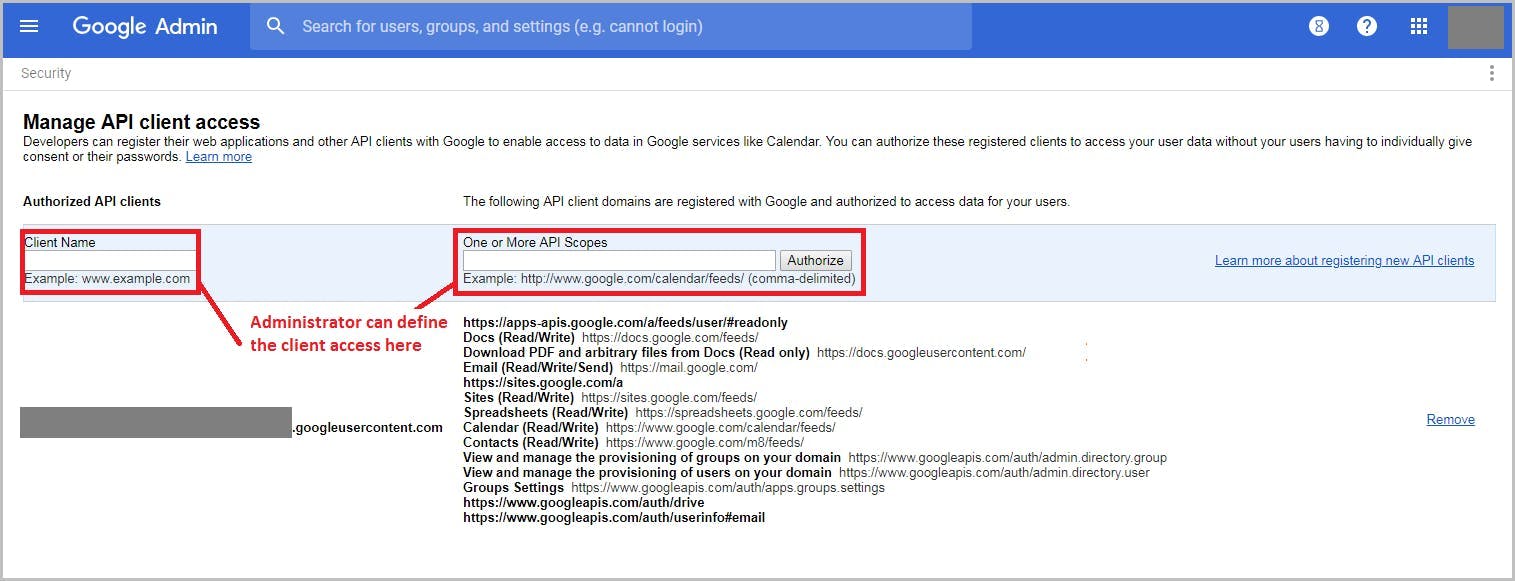
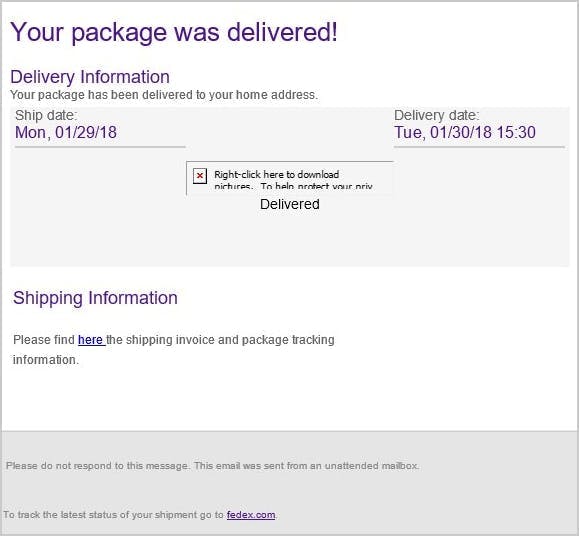
15. Communicate the latest attacks
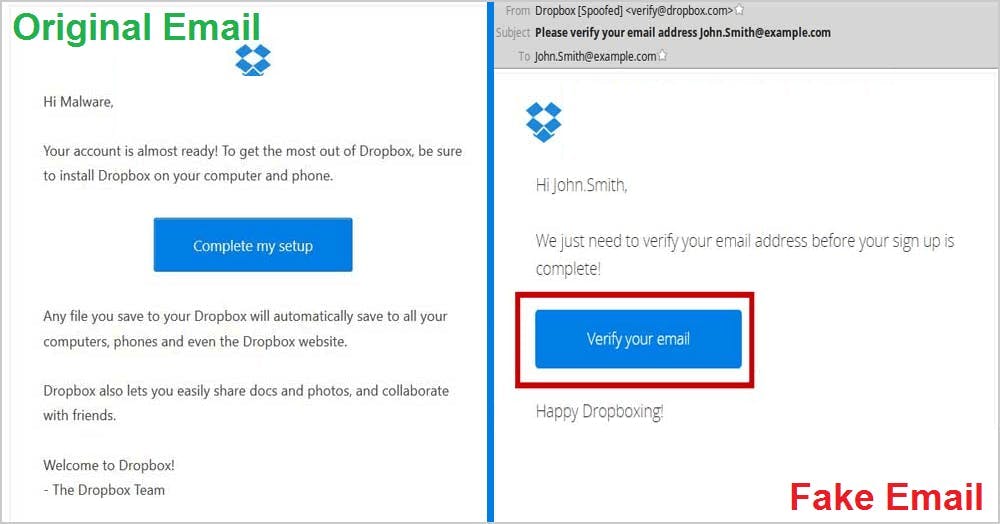
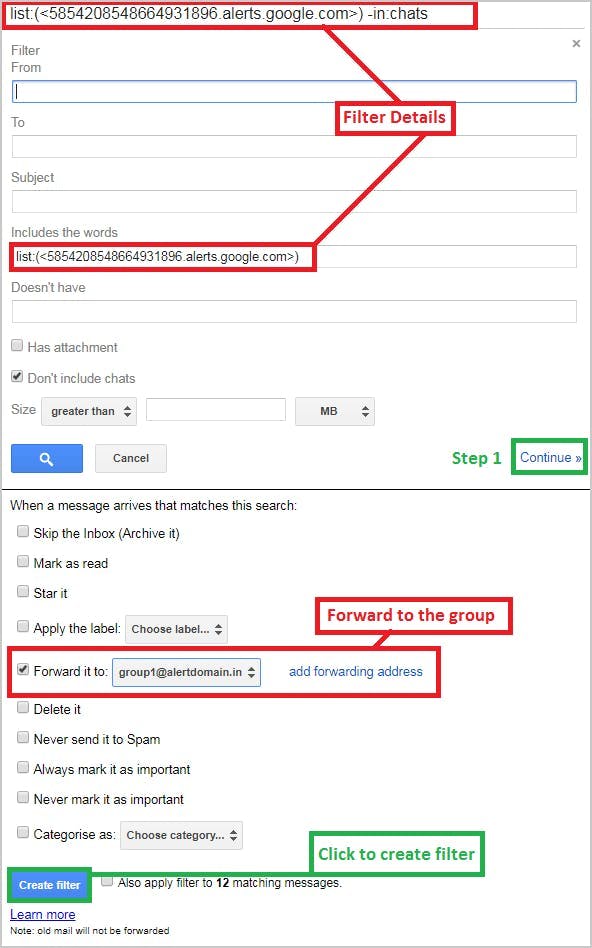
16. Use third-party tools
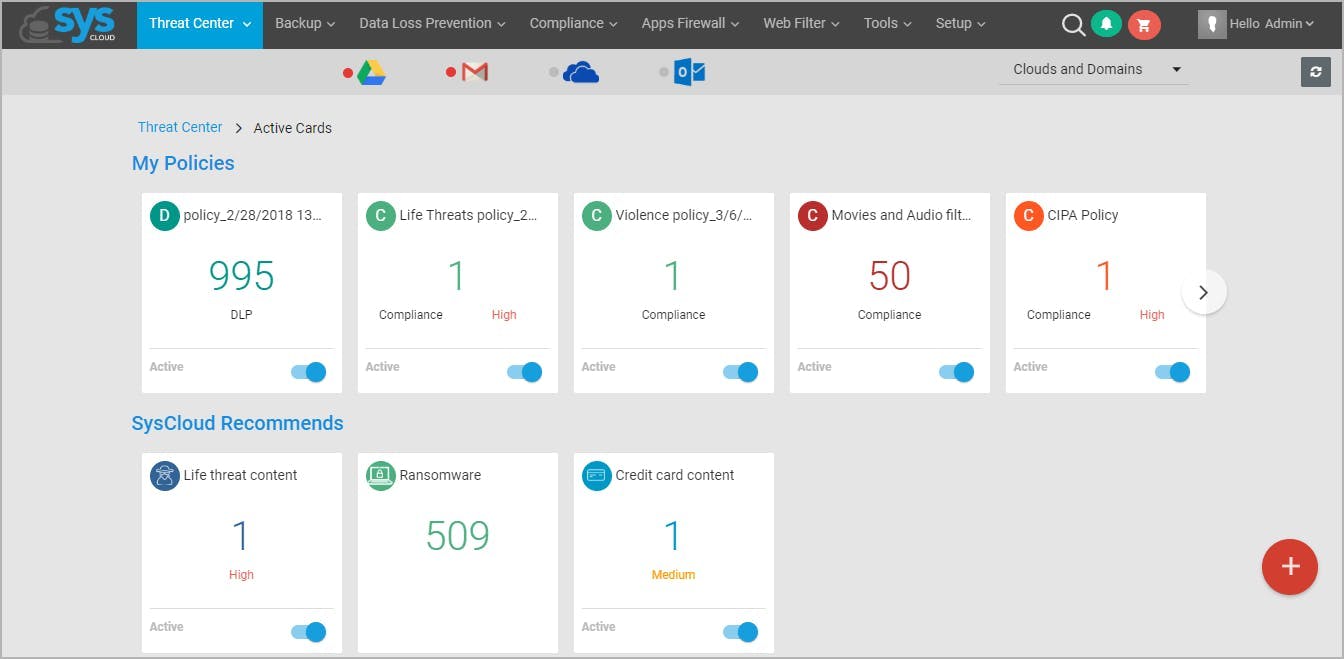
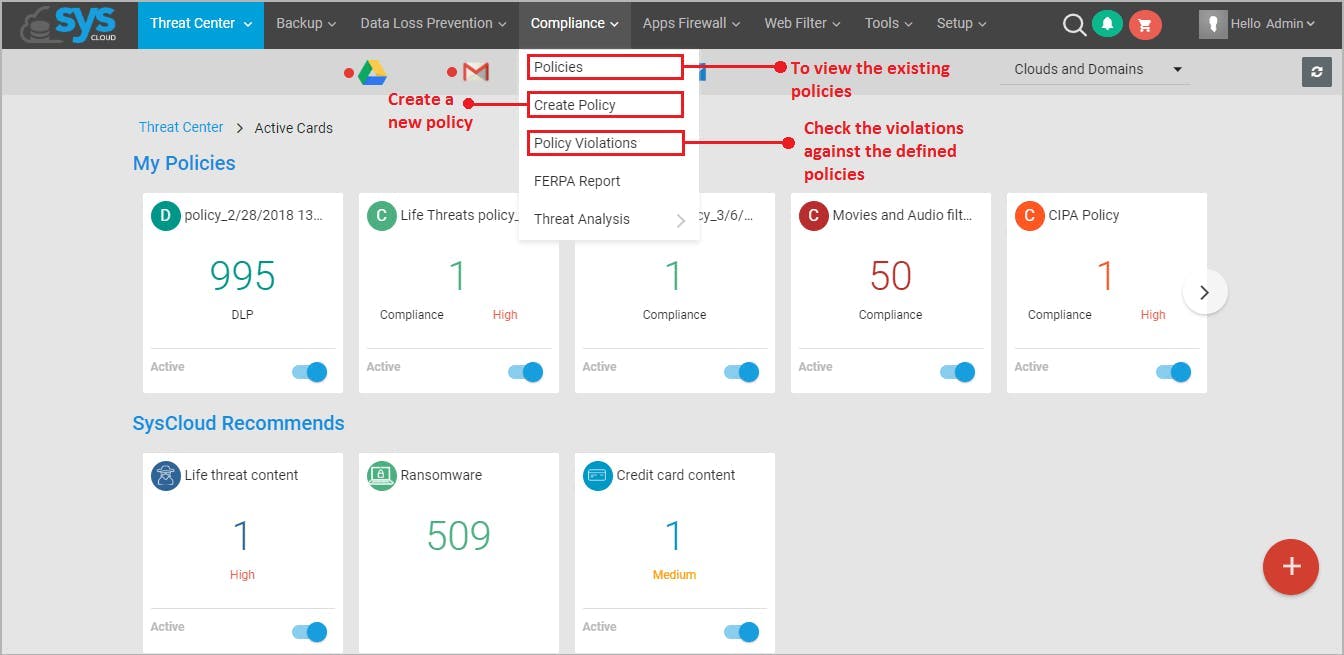
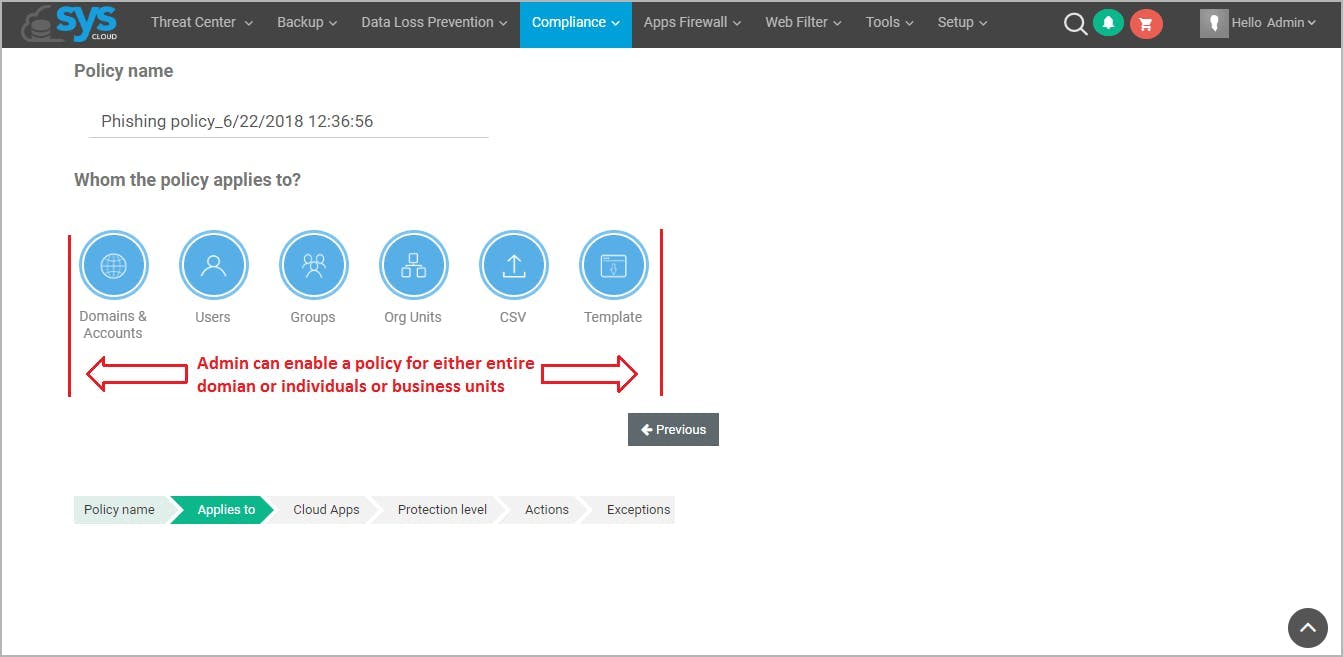
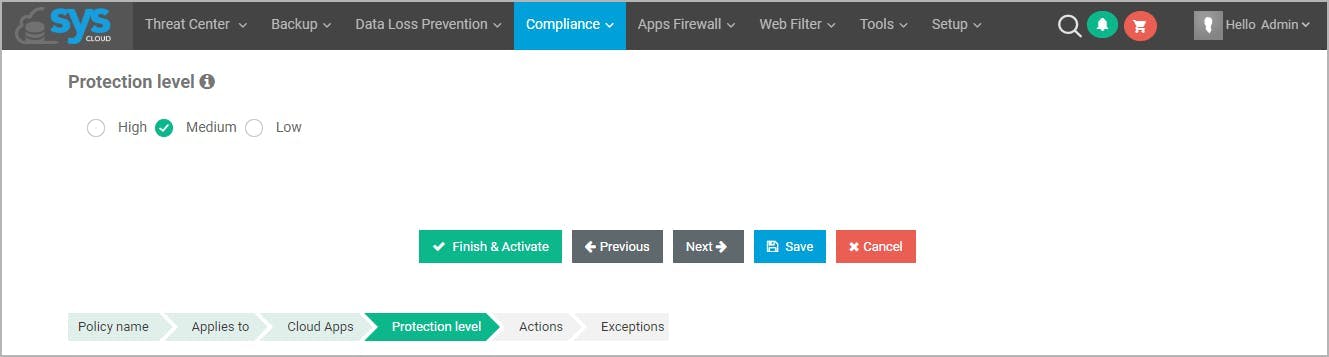
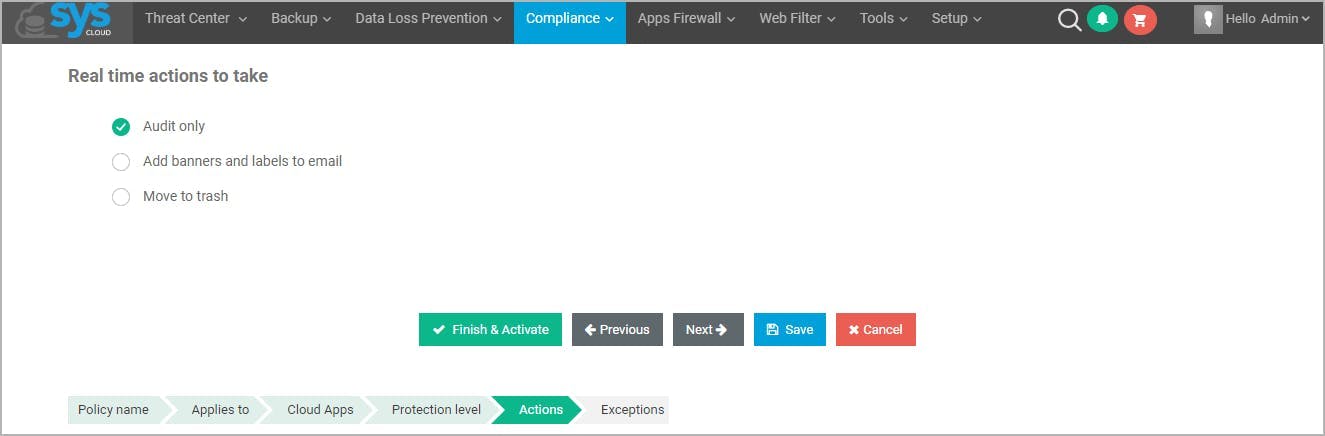
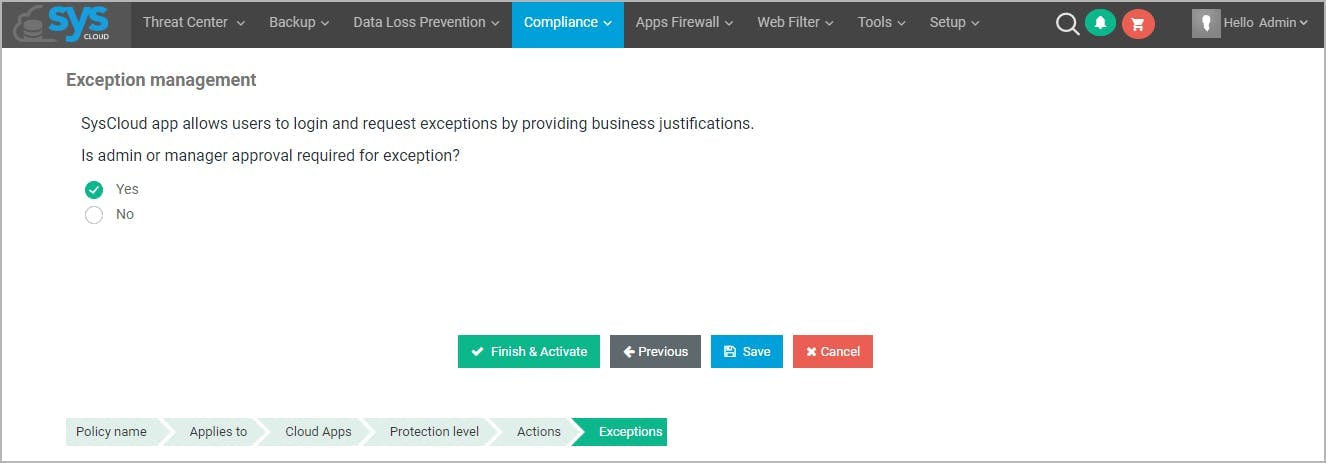
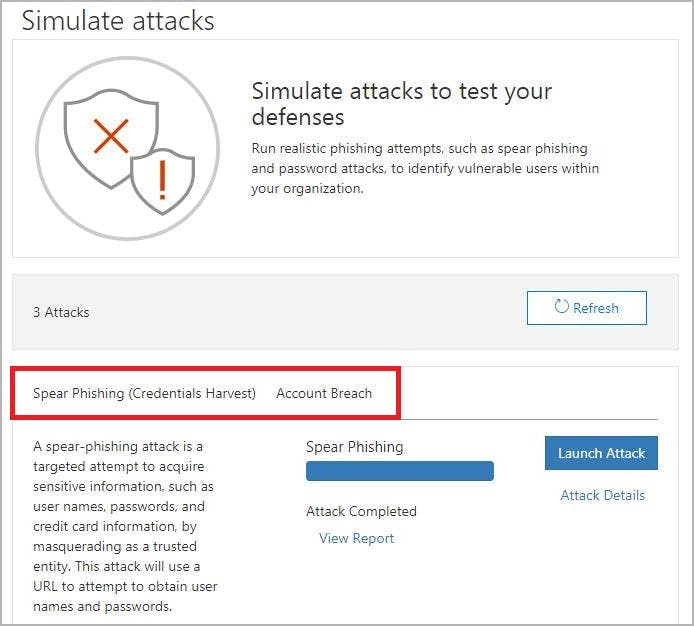
17. Use a phishing simulator