In this article
- Pre-delivery message scanning
- Disable bypass spam filter
- Configure SPF setting
- Configure DKIM setting
- Configure DMARC setting
- Email attachment scan settings
- Gmail spoofing settings
- Security sandbox setting
- SMTP MTA-STS protocol
- Hosted S/MIME
- Spam header settings
- Comprehensive mail storage setting
- Physical security key
- Data backup strategy
Blog Articles
Article at a glance
Enhancing Gmail security settings is crucial for protecting your account from unauthorized access:
- Key settings include enabling two-factor authentication (2FA), regularly updating your password, and reviewing account activity to detect suspicious behavior.
- Other important steps involve managing third-party app access and setting up account recovery options to secure your data.
Read more
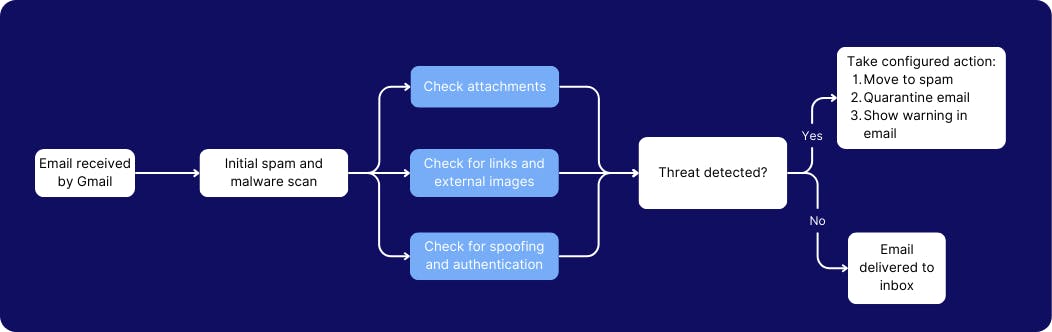
1. Pre-delivery message scanning to prevent phishing and spamming
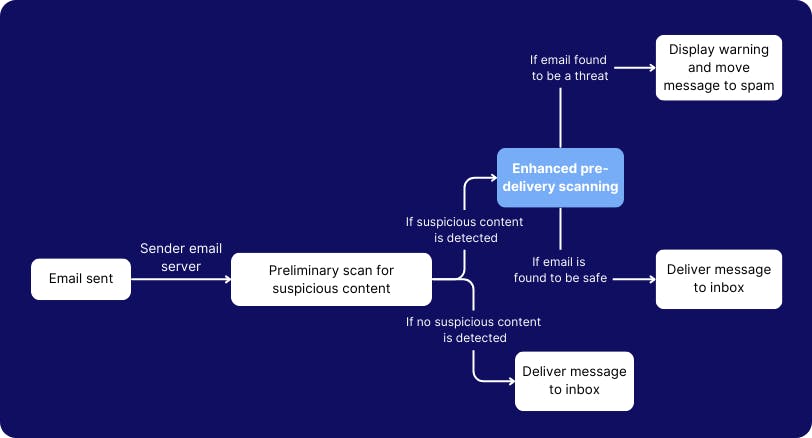
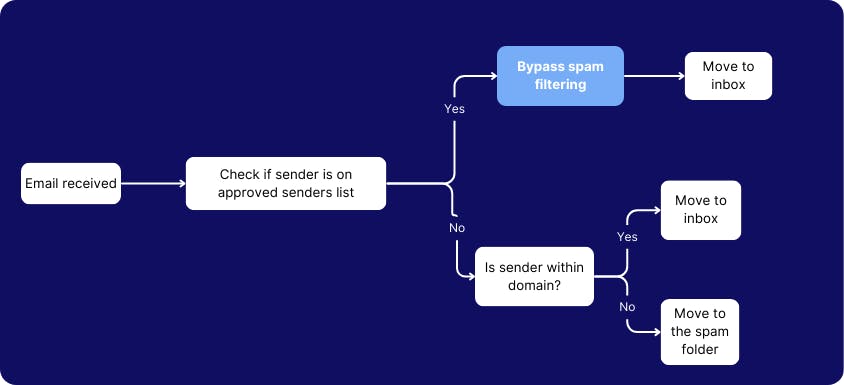
2. Disable bypass spam filter to scan all internal emails and suspicious links
3. Configure SPF setting to receive emails only from designated email servers

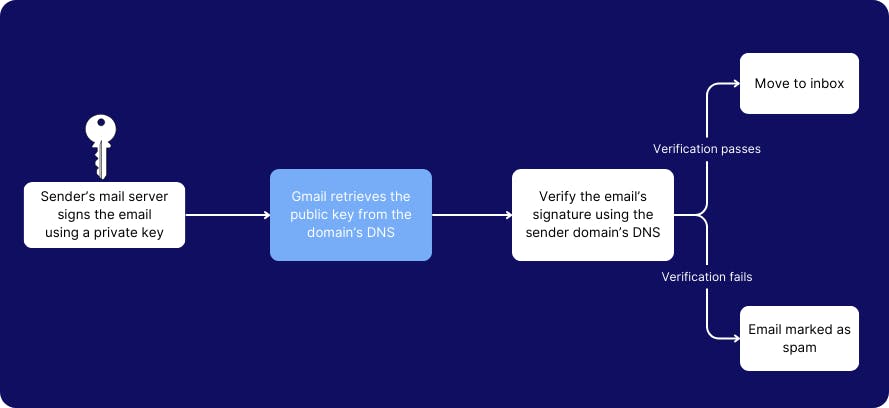
4. Configure DKIM setting to verify email authenticity
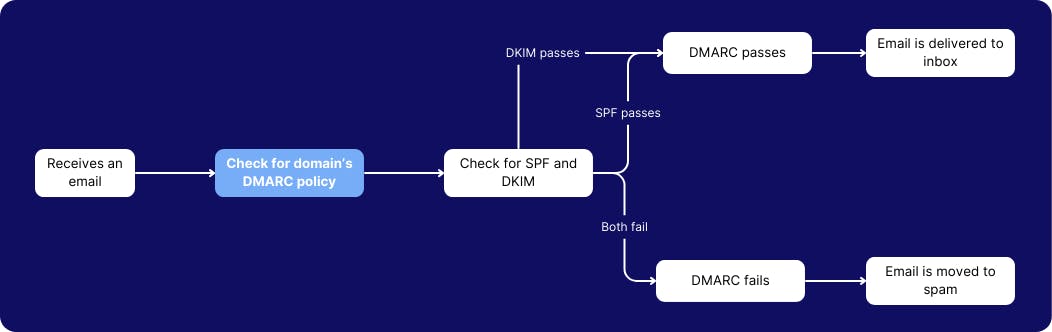
5. Configure DMARC setting to verify the email sender’s domain authenticity
6. Enable email attachment scan settings to scan encrypted attachments and scripts
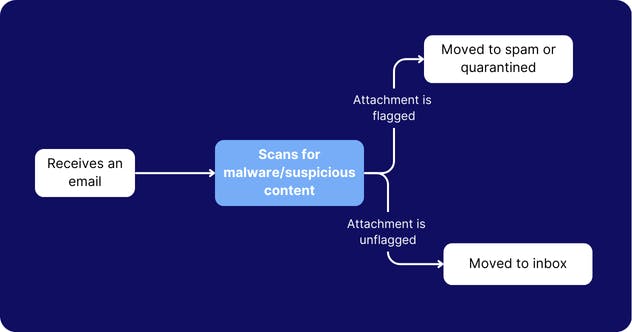
7. Enable Gmail spoofing settings to prevent impersonation attacks
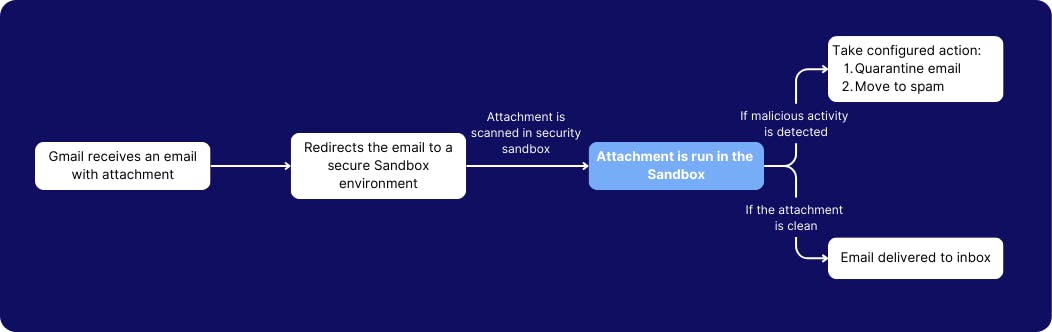
8. Enable security sandbox setting to scan attachments before delivering it
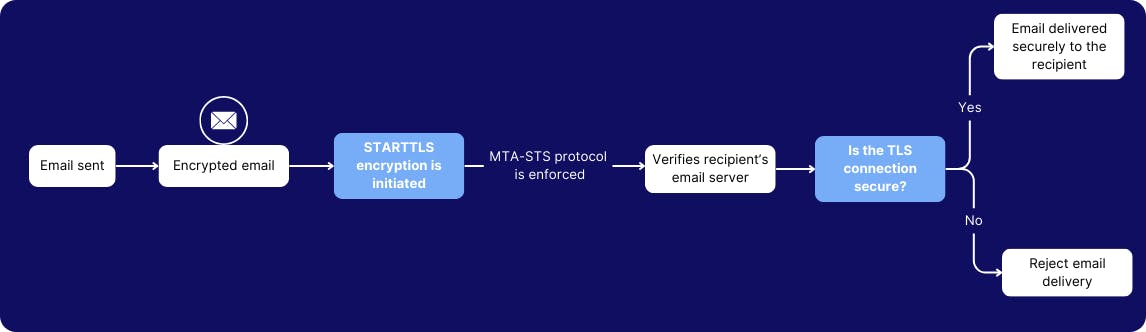
9. Configure SMTP MTA-STS protocol to enforce end-to-end email encryption
10. Enable hosted S/MIME for message encryption
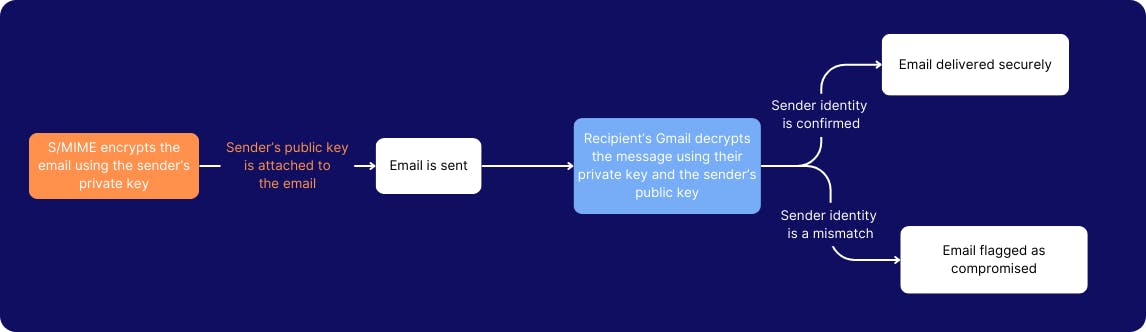
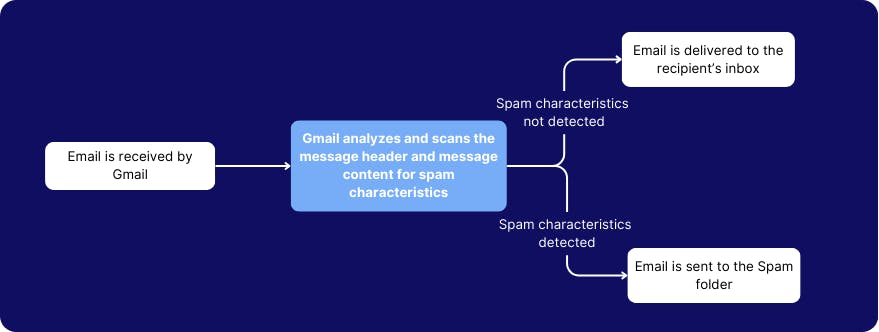
11. Enable spam header settings to maximize spam filtering capacity in all routing rules
12. Enable comprehensive mail storage setting to backup emails from a non-Gmail account
13. Use a physical security key to verify user identity
Data Backup and the Art of Dodging Bullets!
In this article
- Pre-delivery message scanning
- Disable bypass spam filter
- Configure SPF setting
- Configure DKIM setting
- Configure DMARC setting
- Email attachment scan settings
- Gmail spoofing settings
- Security sandbox setting
- SMTP MTA-STS protocol
- Hosted S/MIME
- Spam header settings
- Comprehensive mail storage setting
- Physical security key
- Data backup strategy



